One of the most powerful geological features on the planet is the volcano. Even though they are frequently linked to devastation and natural calamities, they also offer a variety of priceless materials with substantial industrial, scientific, and economic worth. For ages, human civilizations have taken advantage of the natural riches found in volcanoes, which range from fertile soils and geothermal energy to rare earth elements and precious metals. Global industries and economies rely heavily on volcanic resources, such as metals, minerals, gemstones, and geothermal energy. They are rare and extremely precious because of their formation, which is connected to the intricate geological processes of volcanic activity. In this article, we will discuss volcanic resources useful for mankind
What Are Volcano Resources?
The valuable minerals and energy sources produced or impacted by volcanic activity are referred to as volcano resources. These resources include rare earth elements like lithium and zirconium, gemstones like peridot and diamonds, industrial minerals like pumice, perlite, and sulfur, and metals and minerals like gold, copper, silver, and platinum. Along with these material resources, volcanoes also provide geothermal energy, which is a renewable energy source used to heat and generate electricity. Volcanic regions are among the most agriculturally productive places on Earth because of their volcanic soils, which are rich in vital nutrients.
How Volcano Resources Are Formed?
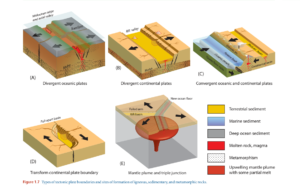
Complex geological processes that take place both during and after volcanic eruptions provide volcanic resources. Magmatic differentiation and crystallization are among the main processes. Rich concentrations of priceless metals like copper, gold, and platinum are produced when various minerals and metals precipitate at different temperatures when lava cools and solidifies inside volcanic chambers. Hydrothermal activity, in which superheated water flowing through volcanic rock fissures dissolves and redeposits minerals to form ore bodies rich in lead, silver, and gold, is another significant process.
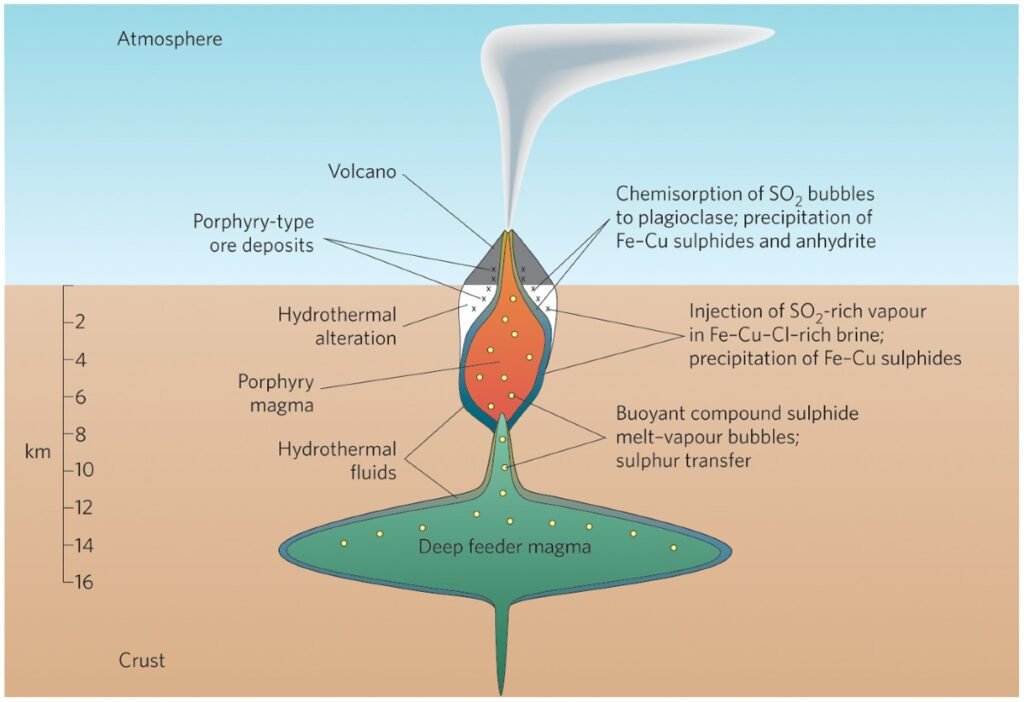
Volcaniclastic sedimentation also contributes to resource formation. Volcanic ash and rock fragments settle and become compacted over time, forming sedimentary layers rich in pumice, perlite, and zeolites. In addition, secondary enrichment occurs when weathering and leaching of volcanic rocks concentrate metals and minerals in specific zones, increasing their economic value. These processes create a diverse range of volcanic resources that are essential for modern industries.
Types of Volcano Resources
Metal and Mineral Resources
Some of the world’s most abundant mineral and metal reserves are the result of volcanic activity. Epithermal deposits created by hydrothermal fluids close to volcanic zones are frequently discovered to contain gold and silver. Porphyry copper deposits, which are associated with subduction zone volcanism, are a common source of copper and molybdenum. Ultramafic and mafic volcanic rocks include platinum-group metals (PGMs), such as palladium and platinum. Carbonatite intrusions and volcanic ash are sources of rare earth elements (REEs), including lithium and zirconium. Layered mafic intrusions linked to volcanic activity contain iron, nickel, and chromium.
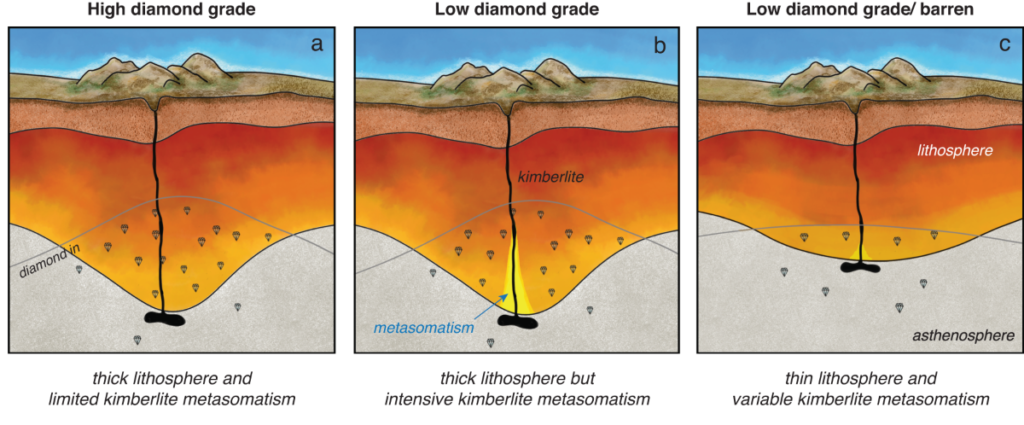
Gemstones and Precious Stones
Certain gemstones form under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions associated with volcanic activity. Diamonds are formed in kimberlite pipes, which are volcanic in origin. Peridot is often found in basaltic lava, while opals and garnets are found in volcanic tuffs and lava flows. These precious stones have been prized for their beauty and rarity for centuries, making them valuable in the jewelry industry.
Industrial Minerals
Numerous industrial materials used in manufacturing, filtration, and construction are produced by volcanic eruptions. Lightweight volcanic rock pumice is used as an abrasive and in building. Perlite is used in horticulture and as insulation since it expands when heated. Zeolites are employed as catalysts in chemical reactions and in the purification of water. Chemicals, fertilizers, and medications are made using sulfur, which is released during volcanic eruptions.

Geothermal Energy
Significant heat is produced below the surface of the Earth by volcanic activity, and this heat can be used to provide direct heating and energy. Geothermal power plants provide a low-carbon, renewable energy source by using steam from volcanic sources to create electricity. By heating buildings, greenhouses, and industrial operations, direct-use geothermal systems lessen dependency on fossil fuels and greenhouse gas emissions.
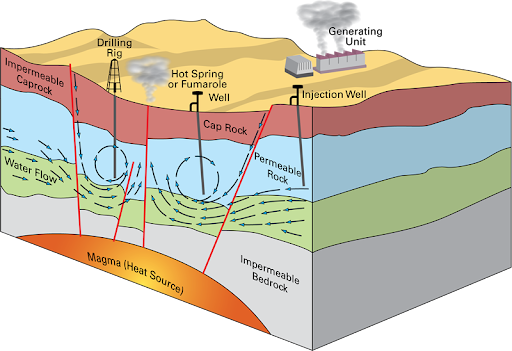
Global Distribution of Volcano Resources
Volcano resources are concentrated in tectonically active areas rather than being dispersed equally throughout the world. One of the most resource-rich volcanic regions is the Ring of Fire, which encircles the Pacific Ocean and has substantial quantities of copper, gold, and geothermal energy. Polymetallic sulfide deposits found on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge were created from hydrothermal vents on the ocean floor. Iceland is a hotspot for volcanic glass and geothermal energy, whereas the East African Rift is recognized for its rare earth materials and geothermal energy. Geothermal resources and volcanic minerals are abundant in volcanic locations such as Central America, Japan, and Indonesia.
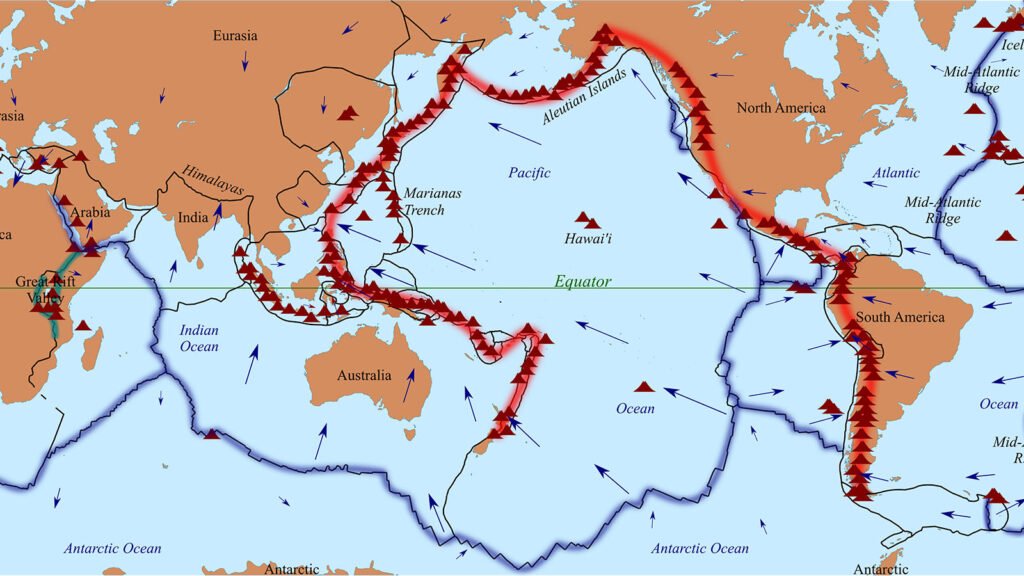
Economic Significance of Volcano Resources
The world economy depends heavily on the resources found in volcanoes. A large amount of the world’s productivity is derived from the mining of gold, silver, and copper in volcanic zones. Electronic components and automotive catalytic converters require platinum-group metals. Electronics, military uses, and renewable energy technologies all depend on rare earth elements. While zeolites are necessary for chemical processing and water purification, industrial minerals like pumice and perlite are frequently utilized in building.
Geothermal energy offers a sustainable and renewable electrical source. For heating and power generation, nations like the Philippines, Iceland, and New Zealand mainly rely on geothermal energy. Some of the world’s most productive agricultural zones are found in volcanic regions, which are supported by volcanic soils that are rich in minerals and nutrients. Beyond simple extraction, volcano resources have economic significance that affects international trade, infrastructural development, and technology.

Challenges and Environmental Concerns
Volcanic resources are valuable economically, but they also provide serious environmental issues and challenges. Risks to infrastructure and human life arise from active volcanic regions’ propensity for earthquakes, eruptions, and the release of hazardous gases. Deforestation, water pollution, and habitat degradation are all consequences of mining and resource extraction. Surface subsidence and mild seismic activity can be caused by geothermal plants.
The mining of volcanic resources also raises political and societal challenges. Conflicts over resource management frequently result from the location of resource-rich volcanic zones in politically unstable areas. Mining and geothermal projects have the potential to uproot indigenous tribes and cause them to lose their ancestral lands. To reduce these adverse effects, environmental laws and sustainable behaviors are crucial.
Future of Volcano Resources
Sustainable methods and technology improvements are key to the future of volcano resources. New sources of rare earth elements and valuable metals may become available through deep-sea mining of polymetallic sulfide deposits near hydrothermal vents. With the use of advanced deep-sea mining equipment, extraction will be possible with little harm to the ecosystem. By increasing geothermal energy production’s efficiency and reach, enhanced geothermal systems (EGS) are making it possible to generate electricity in areas devoid of naturally occurring volcanic activity.

Reducing the environmental impact of mining requires sustainable practices, such as recycling metals and minerals and using environmentally friendly extraction techniques. Exploration and exploitation of volcanic resources are being driven by the growing need for high-tech materials and renewable energy. Volcanic resources will be essential to supplying the world’s expanding resource needs while juggling social and environmental issues.




you got a very fantastic website, Glad I found it through yahoo.